Leadership
Change in digital transformation requires balancing technical excellence with empathetic change leadership 🚀.
The Change Leadership Curve 📈
Every new system creates temporary productivity loss. Understanding these emotional phases is crucial for effective change leadership:
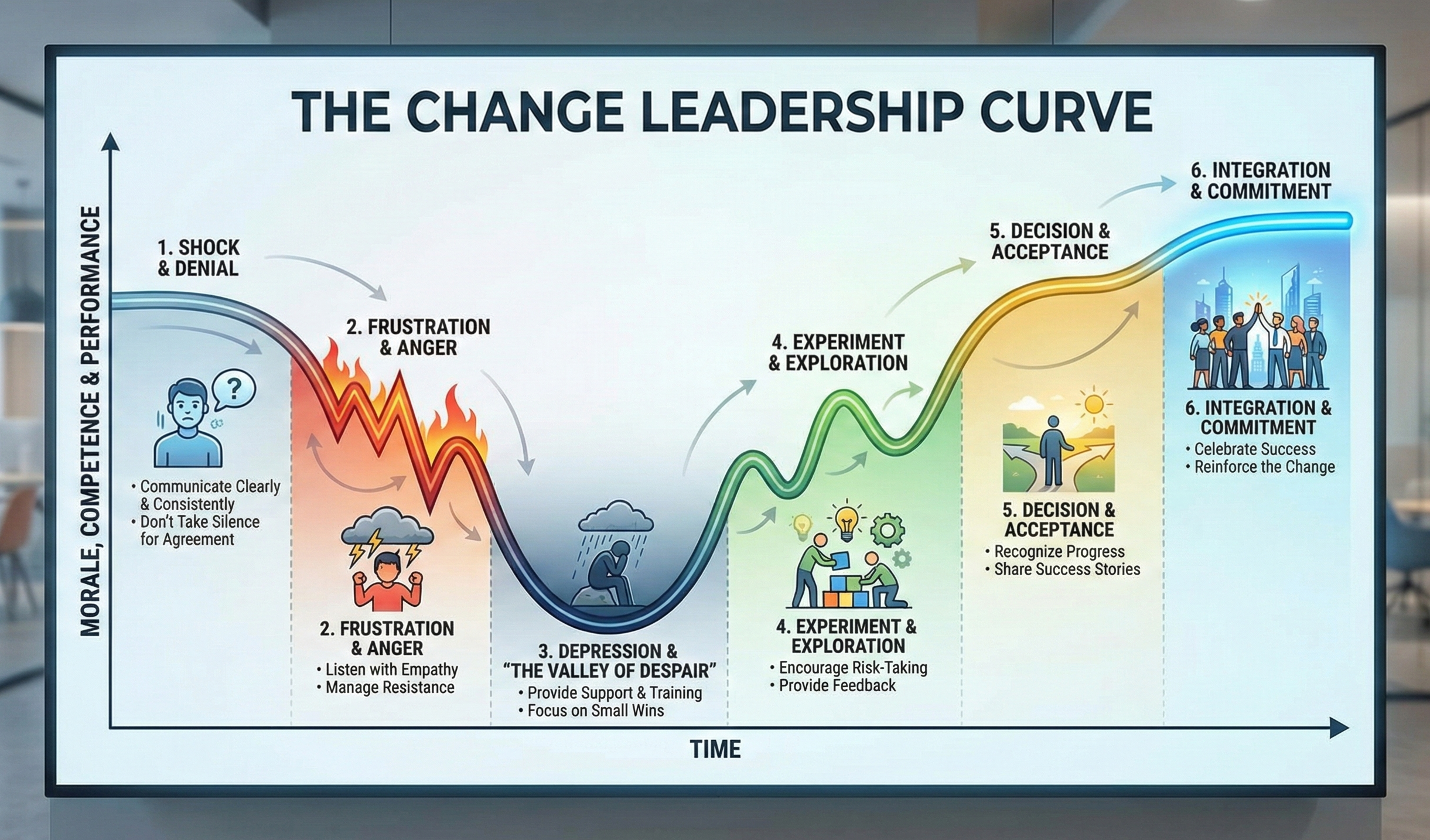
The Change Leadership Curve: Productivity temporarily drops during change management before reaching new levels of effectiveness.
The Challenge of IT Change in Organizations
Digital transformation in organizations is fundamentally a cultural challenge, not just a technical one. In IT environments, resistance to new services often stems from communication gaps between IT departments and business units.
Common Obstacles:
- Cultural Silos: Separation between central IT and decentralized departments
- Lack of Participation: Solutions developed “over the heads” of end users
- Communication Deficits: Technical focus instead of benefit-oriented arguments
Understanding Each Phase of the Change Leadership Curve
1. Shock Phase 🆘
- Reaction: Surprise at sudden IT changes
- Leadership Action: Transparent announcements at least 4 weeks in advance
2. Rejection Phase 🚫
- Reaction: “The old system was better”
- Leadership Action: Focus on comparisons showing concrete improvements
3. Insight Phase 💡
- Reaction: Understanding necessity but frustrated by learning curve
- Leadership Action: Massive training offerings and support hotlines
4. Valley of Tears 😢
- Reaction: Lowest productivity point
- Leadership Action: Leadership must be present, admit mistakes, stay the course
5. Experimentation Phase 🧪
- Reaction: Discovering new workflows
- Leadership Action: Share best practices from different departments
6. Realization Phase ✅
- Reaction: Getting used to the new normal
- Leadership Action: Collect feedback for next optimization cycle
7. Integration Phase 🎯
- Reaction: New standard established
- Leadership Action: Celebrate success and anchor the process
Strategic Recommendations for IT Change Leadership 📋
1. Early Participation 🤝
Establish “Key User Networks” across departments already in the pilot phase. Priority: High
2. Benefit-Oriented Storytelling 📖
Move away from feature lists toward answering: “How does this IT tool save me 15 minutes per day?” Priority: Medium
3. Iterative Rollouts 🔄
Avoid “Big Bang” scenarios. Introduce in phases with visible “Quick Wins” for users. Priority: High
4. Strengthen Error Culture 🛠️
Institutionalized retrospectives after IT outages. Focus on process optimization instead of blame. Internal Goal
5. Training Multipliers 📚
Training-of-Trainers approach to bring IT knowledge directly into teams. Structure
6. Transparency During Outages 🔍
Proactive status dashboards and clear timelines reduce anxiety and resistance during maintenance windows. Trust Building
Leadership Profiles in IT Organizations 🎭
The “Administrator” Profile
- Focus: Availability, cost control, rigid processes
- Characteristics: High stability, high efficiency, low innovation, low agility
The “Transformer” Profile
- Focus: Innovation, user-centricity, agile mindset
- Characteristics: Balanced stability, high innovation, high empathy, high agility
Modern IT leadership requires transitioning from pure administration to transformation - balancing stability (security/uptime) with agility (innovation/growth).
Key Leadership Competencies 🌟
Balance Between:
- Stability: Ensuring reliable, secure systems
- Innovation: Embracing new technologies and approaches
- Efficiency: Optimizing processes and resource usage
- Empathy: Understanding and addressing user needs
- Control: Maintaining appropriate governance
- Agility: Adapting quickly to changing requirements
The most effective IT leaders cultivate all these competencies, knowing when to emphasize each based on organizational context and transformation goals.
This framework draws from practical experience in IT change leadership and is designed to support strategic planning and training in organizational IT leadership.